We Are A Group
SD Wan
Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN)
CloudAccess Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) is a deployment approach that allows organizations with multiple branches to securely connect via public broadband options like Fiber, Cellular, Fixed Wireless, Cable, and xDSL into a private WAN.
The CloudAccess SD-WAN Orchestrator simplifies the integration of branch locations by managing networking and rules between sites. This enables users at one branch to access resources from other branches, even across different subnets.
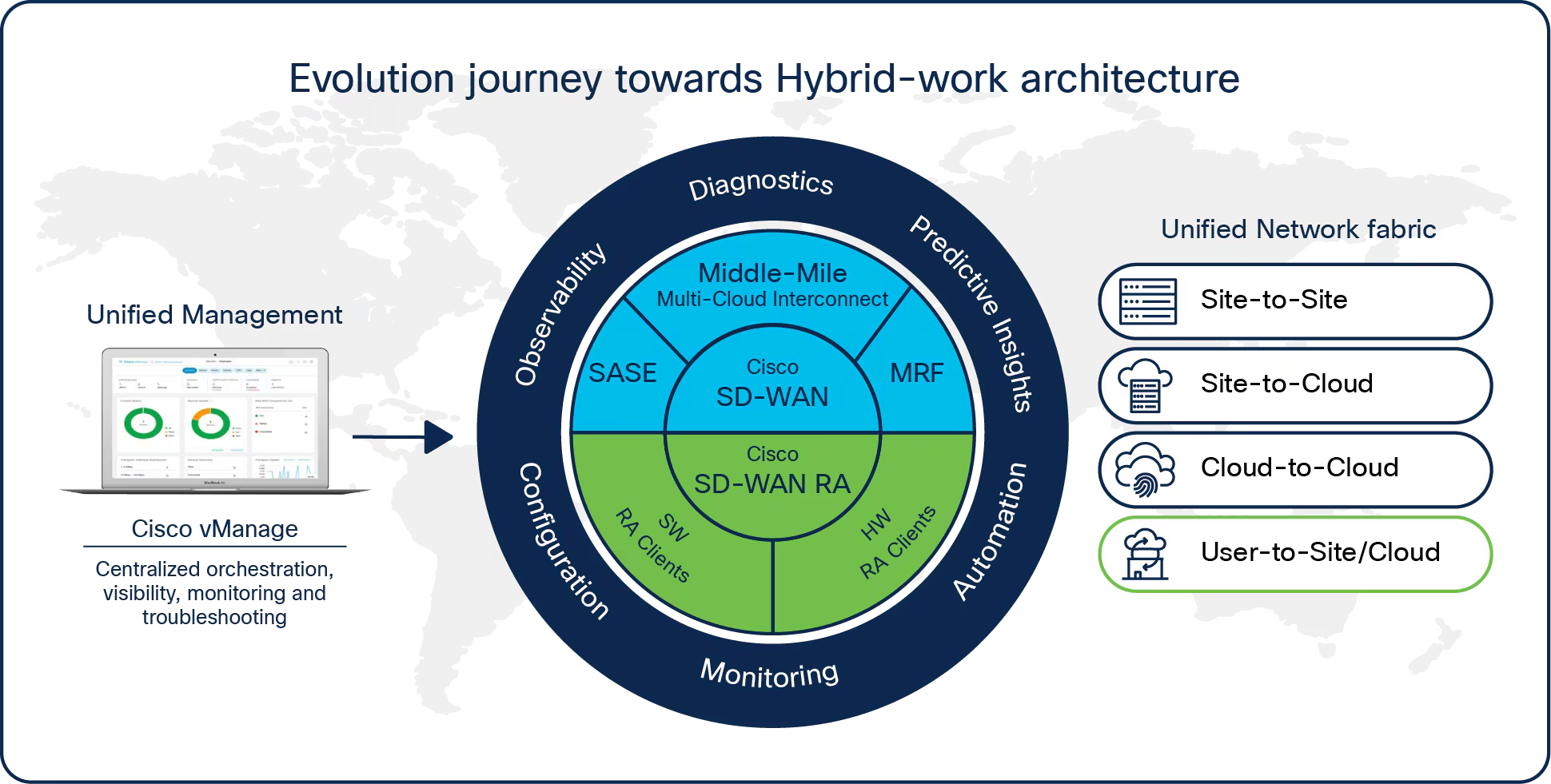
Software Defined Wide Area Network Topology
Traditional switch-based WAN designs are becoming obsolete. SD-WAN is built to connect multiple branch offices, remote workers, distant users, and mobile teams worldwide using broadband connections. With SD-WAN, users can access remote apps hosted in public or private clouds, benefiting from improved application performance and streamlined management of SaaS services such as UCaaS and Office 365.

How does SD-WAN work?
SD-WAN Remote Control with an Orchestrator
Software Defined Wide Area Network – Alternative to MPLS
SD-WAN is a great alternative to MPLS because management and deployment can be configured remotely.
- Modify routing rules at one or multiple locations within minutes
- Use affordable hardware at customer sites
- Maximize existing broadband connections at each branch
- Ensure secure WAN access in remote locations
- Apply Quality of Service (QoS) for broadband performance
- Boost bandwidth at branch sites with bonded internet connections
- Offer backup internet via cellular networks like 3G, 4G, LTE, and 5G
Analytics galore: Network alerts and link health monitoring
Cloud Access offers the insights you need to understand customer demands while delivering real-time data on site performance.

Why offer Cloud Access Software Defined Wide Area Networks?
Until recently, SD-WAN benefits were mostly accessible to enterprises and Fortune 500 companies. We believe these advantages should be available to all, regardless of resources. Cloud Access provides a white-labeled SD-WAN platform, empowering independent providers to offer SMBs and remote work clients a variety of network solutions.
Cloud Access is a white-label SD-WAN service that providers can rebrand. It operates on the provider’s infrastructure, using their own IP blocks, and runs on x86 hardware with different processor and cost options. ISPs can either source their own hardware or purchase equipment from Vutele services India to control expenses.
Benefits of Cloud Access
- White Label – Rebrand it as your own
- Hosted within provider’s infrastructure
- Cost-effective hardware options
- Zero-touch deployment
- Remote configuration and management
- Bonded Internet Connectivity for enhanced bandwidth
- Backup Internet Connectivity for high availability
- Site-to-site encryption
- Quality of Service (QoS) for prioritizing critical applications

